Knock Sensor: How It Works, Common Issues, and How to Fix Them
The knock sensor is an important monitoring device in modern internal combustion engines. Mounted directly on the car engine block, it listens for unusual sounds, specifically engine knocking or "pinging", and sends a signal to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the ignition timing accordingly.
This helps protect the engine from serious damage and maintains efficient performance. In this article, we’ll explain how knock sensors operate, what happens when they fail, and what to do if your vehicle displays a fault code like P0325.
What does a knock sensor do?
When combustion in the engine cylinders doesn’t happen as intended, such as when the air-fuel mixture ignites too early due to excessive heat, it creates sharp pressure waves. These generate a distinctive knocking sound. The knock sensor detects this sound and alerts the ECU, which responds by adjusting the ignition timing to prevent damage.
The sensor is usually a piezoelectric device that converts vibrations into electrical signals. It may have one or two terminals. A single-terminal sensor grounds itself through its body, while a dual-terminal design includes both a ground and a signal wire. These signals are monitored by the Active Control Engine Mount (ACM) or ECU, which expects a stable signal under normal conditions. Irregularities indicate either knocking or a sensor malfunction.


Common knock sensor defect symptoms
A faulty knock sensor often triggers the check engine light on your dashboard. Other symptoms may include:
- Decreased engine performance
- Increased fuel consumption
- Occasional engine misfires
- Hesitation during acceleration
However, in some cases, the only sign may be a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), such as P0325, without any noticeable changes in driving behaviour. The onboard computer will need to be scanned using an OBD2 scanner to find the source of the error.
What does it mean when the error code P0325 is displayed?
The P0325 code indicates a malfunction in the knock sensor circuit, specifically for sensor 1 in bank 1. This can arise from several causes:
- A failed or worn knock sensor
- Damaged or corroded sensor wiring
- Faulty electrical connections
- A defective ECU
In some cases, this issue may be caused by legitimate engine problems, which show symptoms that are similar to a faulty sensor. For example, causes may range from ignition and timing faults to the use of poor-quality fuel.
How to diagnose and repair error code P0325
Before jumping to a replacement, a proper diagnosis is essential to avoid unnecessary expenses. Start with the following steps:
- Visual inspection: Check the sensor’s wiring and connector for any signs of wear, corrosion, or looseness.
- Test the circuit: Use a multimeter or scan tool to check the voltage and signal output.
- Evaluate engine cooling system: Sometimes knocking symptoms stem from overheating. It’s wise to inspect the cooling system and the coolant temperature sensor as part of your diagnosis.
- Test drive and re-scan: After clearing the fault codes, a professional technician will typically take the vehicle for a test drive to confirm whether the fault reoccurs.
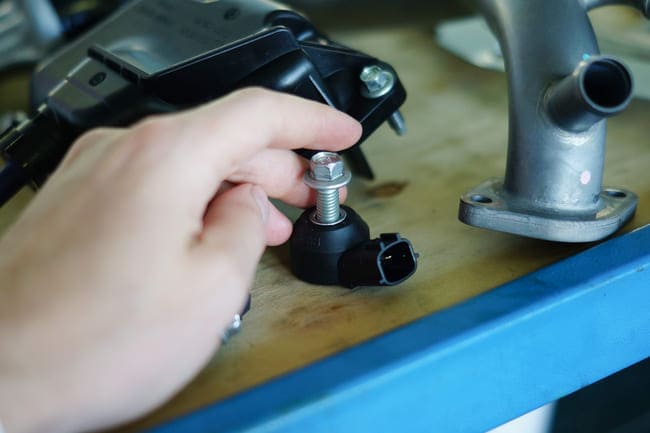

If the sensor proves to be faulty, replacing usually isn’t so complicated. Depending on the vehicle make and model, as well as your experience, you may be able to perform the replacement yourself using basic tools. If you’re unsure, it's best to leave the job to a qualified mechanic.
Can the code disappear on its own?
It’s possible, though unlikely, for the P0325 code to vanish if it was triggered by a temporary glitch. However, ignoring it may lead to undetected knocking and long-term engine damage. Repeated exposure to knocking and irregular combustion can harm pistons, bearings, and other key components, resulting in costly repairs.

Can I drive with code P0325?
While your car might still be drivable, continuing to operate a vehicle with this code is not recommended. Driving with a faulty knock sensor prevents the ECU from adjusting ignition timing to prevent engine damage. If the sensor has failed, replace it as soon as possible.

How much does it cost to replace a knock sensor?
The cost of replacing a knock sensor depends on your vehicle make and whether you choose to do it yourself or hire a professional. The sensor itself typically starts at around £33. Labour charges will vary depending on your car model and your mechanic’s hourly rate.
A DIY replacement can save you money, especially if the sensor is easy to access. However, some vehicles require partial engine disassembly, which is better handled by an experienced mechanic.
A malfunctioning knock sensor might not be the only issue if your engine is displaying performance problems. It’s useful to understand related parts such as the crankshaft sensor or O2 sensor. Working together, these sensors provide vital data to the ECU, helping ensure your car runs smoothly.
Final summary
The knock sensor is a vital line of defence for your engine, safeguarding it against abnormal combustion that could lead to serious damage. Understanding how it works, recognising the symptoms of failure, and taking prompt action when issues arise can save you time, money, and headaches in the long run.
Crankshaft Sensor: what you need to know
Top products