Table of Contents
Loss of power in car: causes and malfunctions
After driving your car on a regular basis over many months and years, you get to know it pretty well. That’s why it usually doesn’t take a driver long to spot an abnormal loss of engine power. For example, you may notice that your car feels sluggish when you’re cruising down the motorway or that it isn’t accelerating as it should be. The possible causes of a loss of engine power are numerous, but the good news is that they are treatable.
The first step to getting back on the road is to figure out why your car loses power while driving. Once you have a proper diagnosis, you can go ahead and plan the repairs, as well as figure out your budget. This guide will cover the most common causes and malfunctions related to power losses.
Why is my car losing power?
In most cases, the problem lies somewhere within the fuel supply or ignition system. In order to produce power from combustion, the engine needs a consistent supply of fuel and air. Interruptions to the flow of fuel and air, such as those caused by blockages or electrical faults, are therefore the main culprits for a loss of engine power.
Sold by AUTODOC Sold by AUTODOC Sold by AUTODOC Sold by AUTODOC Sold by AUTODOC  PURFLUX Fuel filter
Filter Insert
PURFLUX Fuel filter
Filter Insert
 BOSCH Fuel filter
with integrated pressure regulator, In-Line Filter, 8mm, 8mm
BOSCH Fuel filter
with integrated pressure regulator, In-Line Filter, 8mm, 8mm
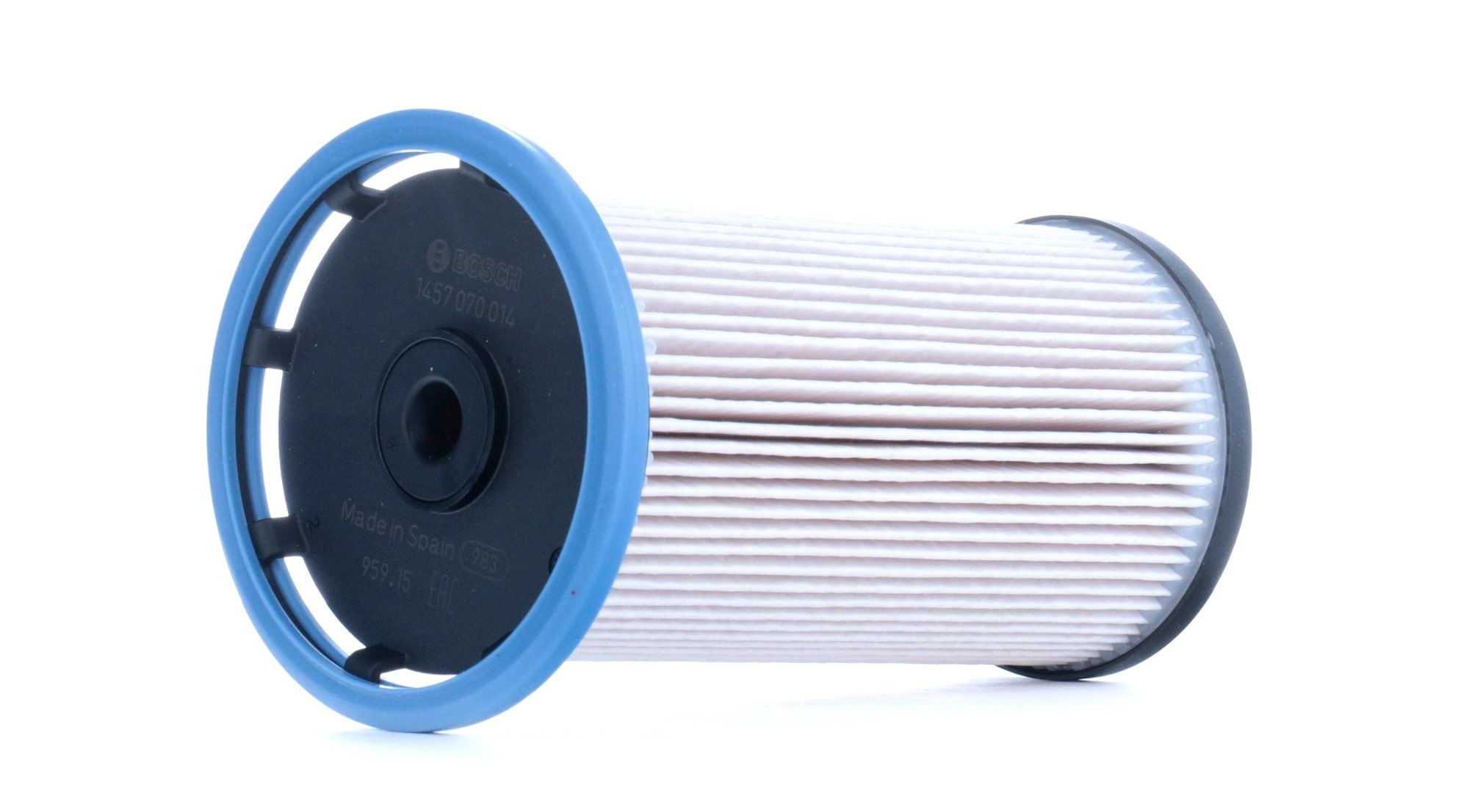 BOSCH Fuel filter
Filter Insert
BOSCH Fuel filter
Filter Insert
 MANN-FILTER Fuel filter
In-Line Filter, 10mm, 8mm
MANN-FILTER Fuel filter
In-Line Filter, 10mm, 8mm
Common causes and malfunctions:
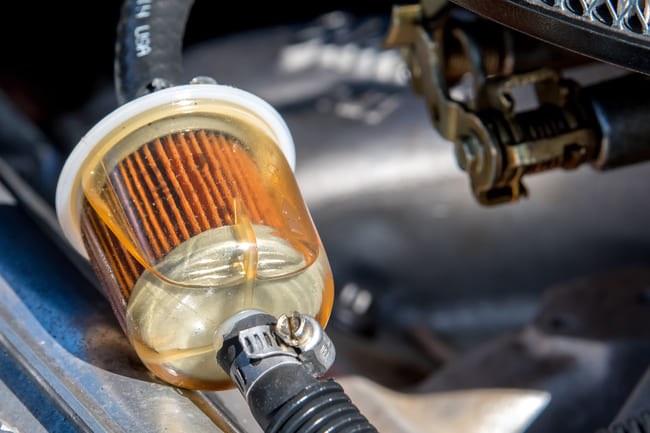
- A clogged fuel filter
If the fuel filter gets clogged up by dirt, debris and other contaminants, it’s possible that the engine won’t receive enough fuel. This may result in poor acceleration, misfires, sudden drops in power, and stalling. It’s rare that the blockage stops the engine from starting altogether, but you may find that it takes longer to crank the engine before it starts.
- A failing fuel pump
The pump needs to be able to produce enough power to force the petrol or diesel through the fuel supply system and into the engine. Sometimes it fails to do so as a result of an electrical fault or excessive wear. An overused car fuel filter can actually cause the pump to fail due to the increased pressure and force needed to push the fuel through it.

- Filthy fuel injectors
These components are responsible for injecting the fuel into the combustion chambers, where it is mixed with air and ignited. A precise and extremely high amount of pressure is required to do this on time every time. Disruptions can result in a loss of power and damaged engine pistons.
This is often the result of a buildup of carbon deposits, blocking the injector nozzles. A dirty fuel system or use of poor-quality fuel will ultimately speed up the formation of carbon deposits. You may be able to prevent this from happening again by cleaning out the system using an effective engine and fuel system cleaner.
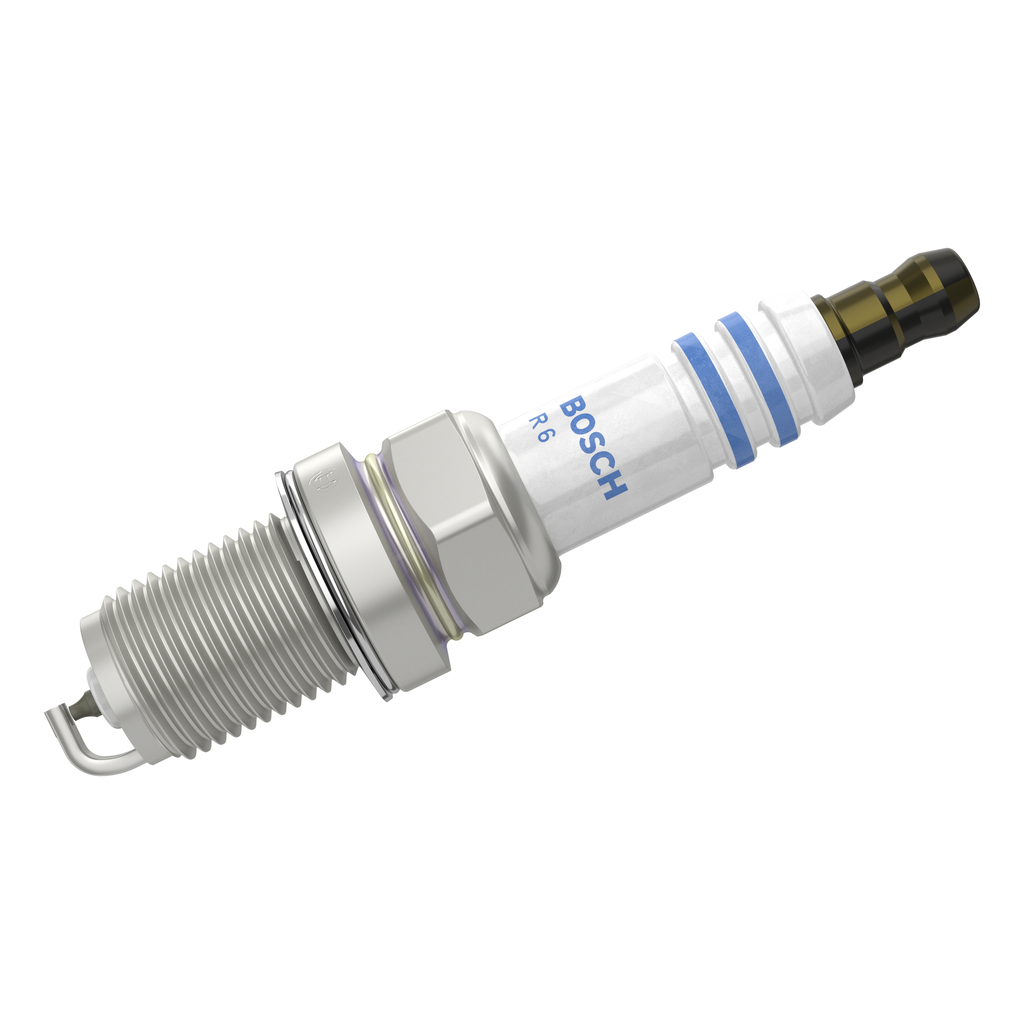
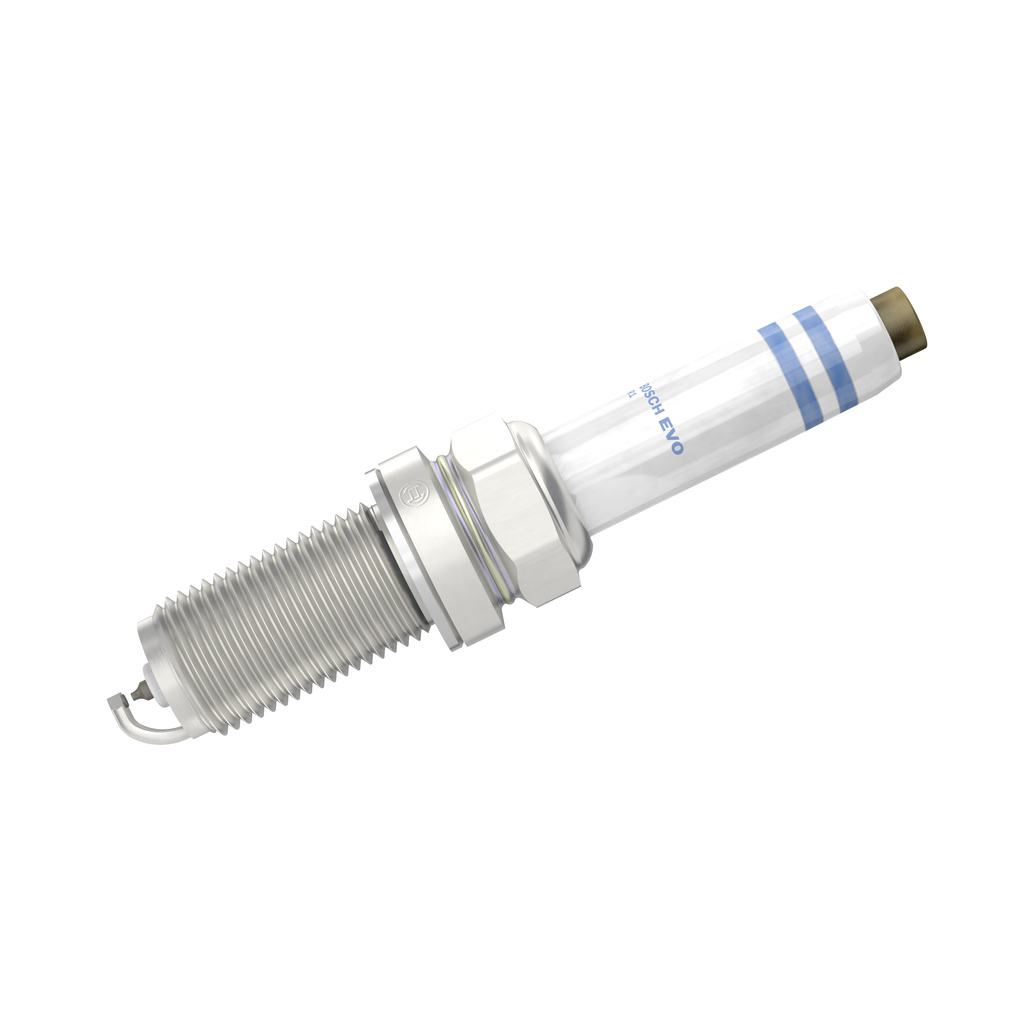
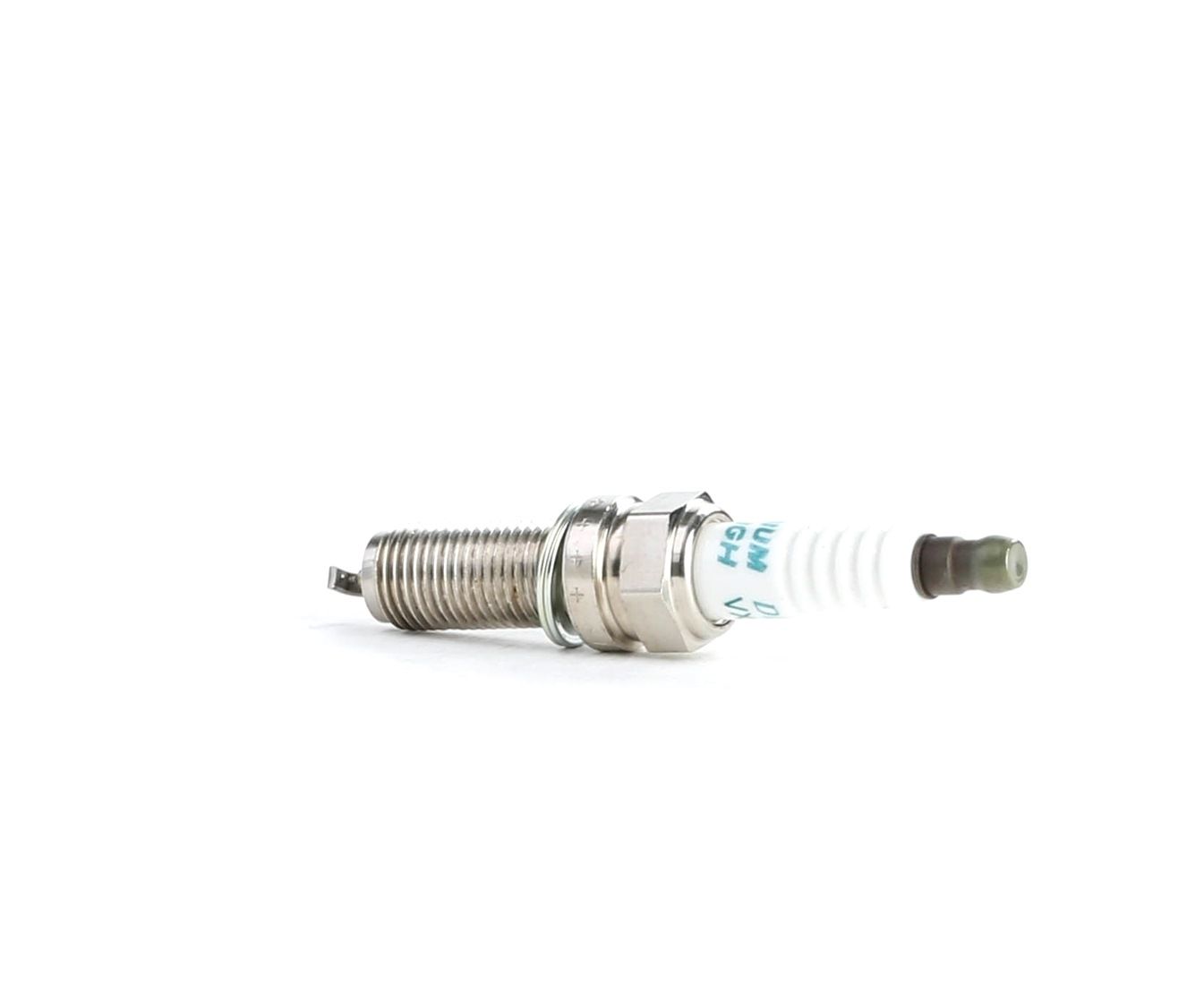
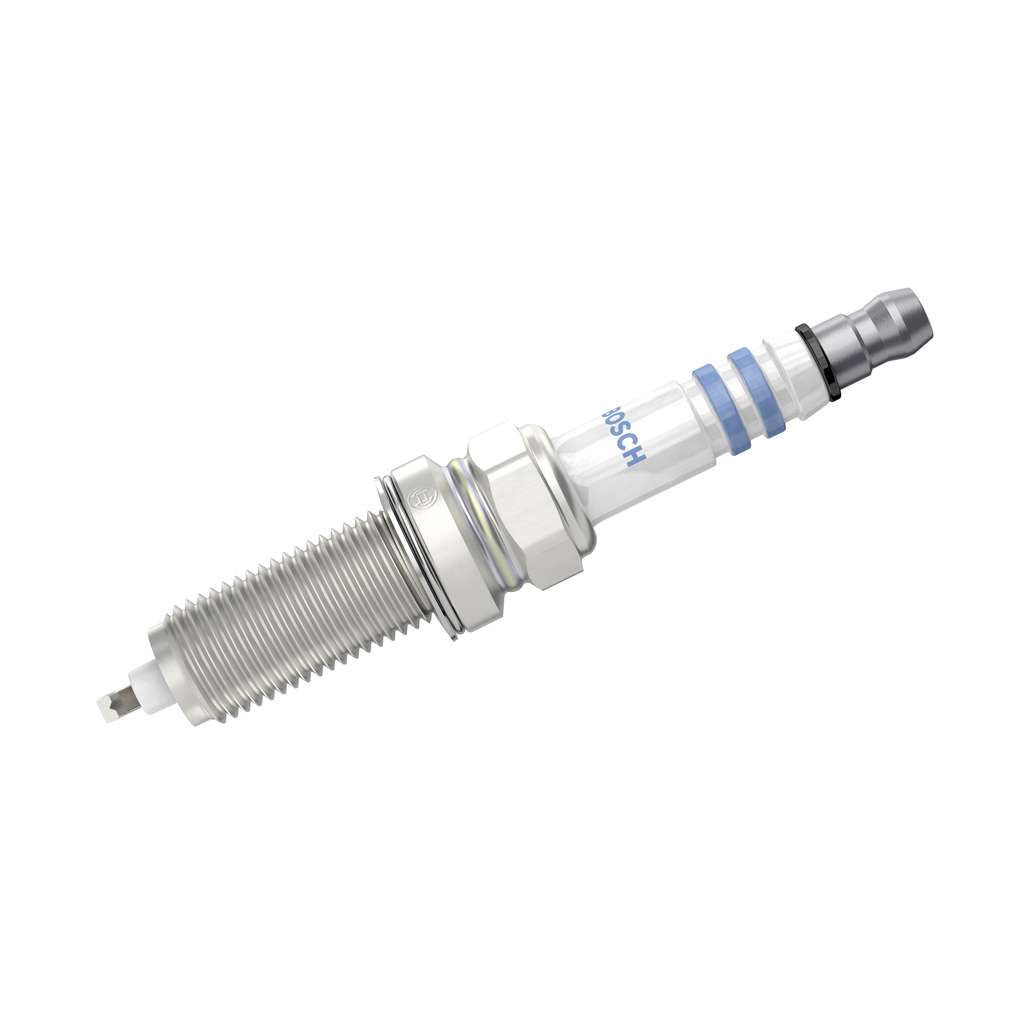
- Faulty spark plugs
Spark plugs ignite the fuel, making them critical for the combustion process. Eventually, these parts will wear out, potentially causing misfires, reduced engine performance due to power losses, and knocking or rattling noises. You should replace your spark plugs on time according to the intervals specified by the car manufacturer.
Sold by AUTODOC Sold by AUTODOC Sold by AUTODOC Sold by AUTODOC Sold by AUTODOC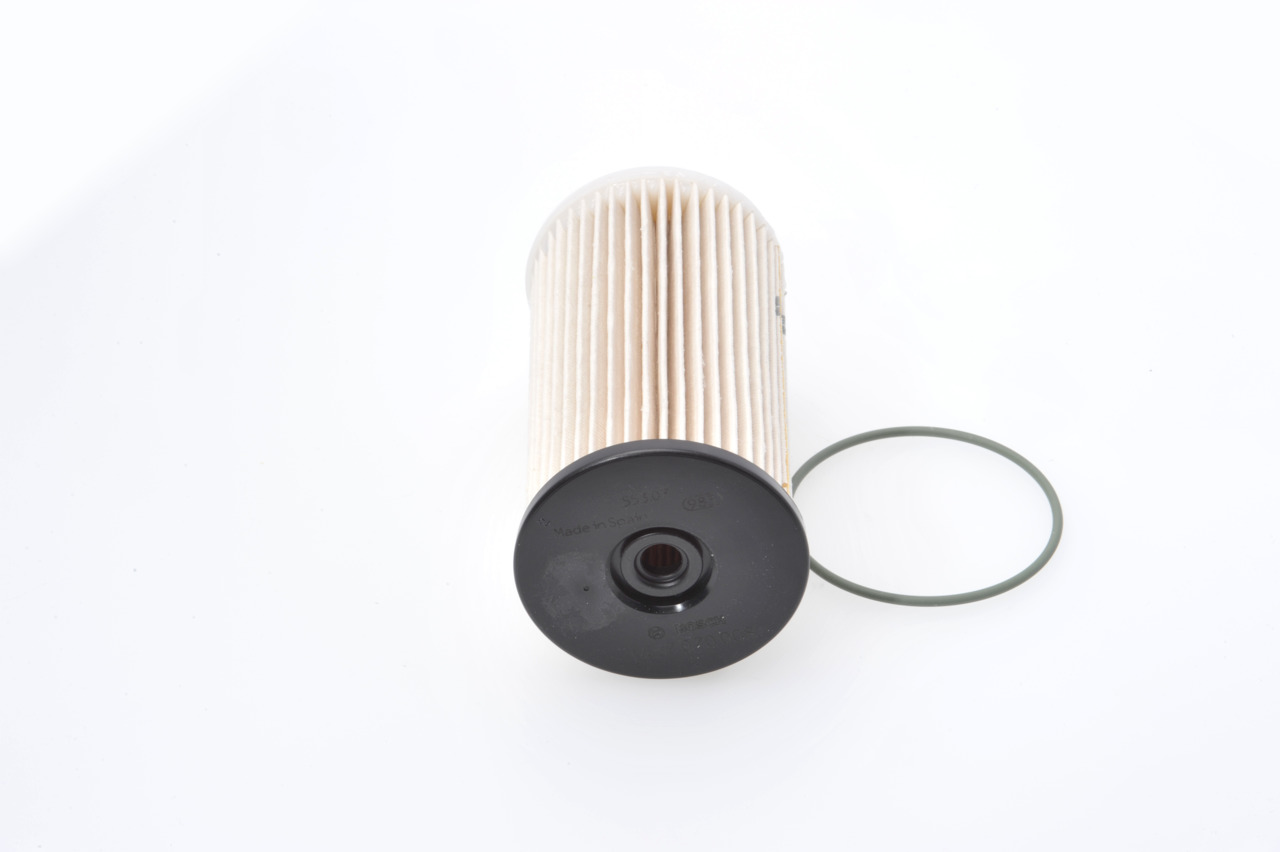  BOSCH Fuel filter
Filter Insert
BOSCH Fuel filter
Filter Insert
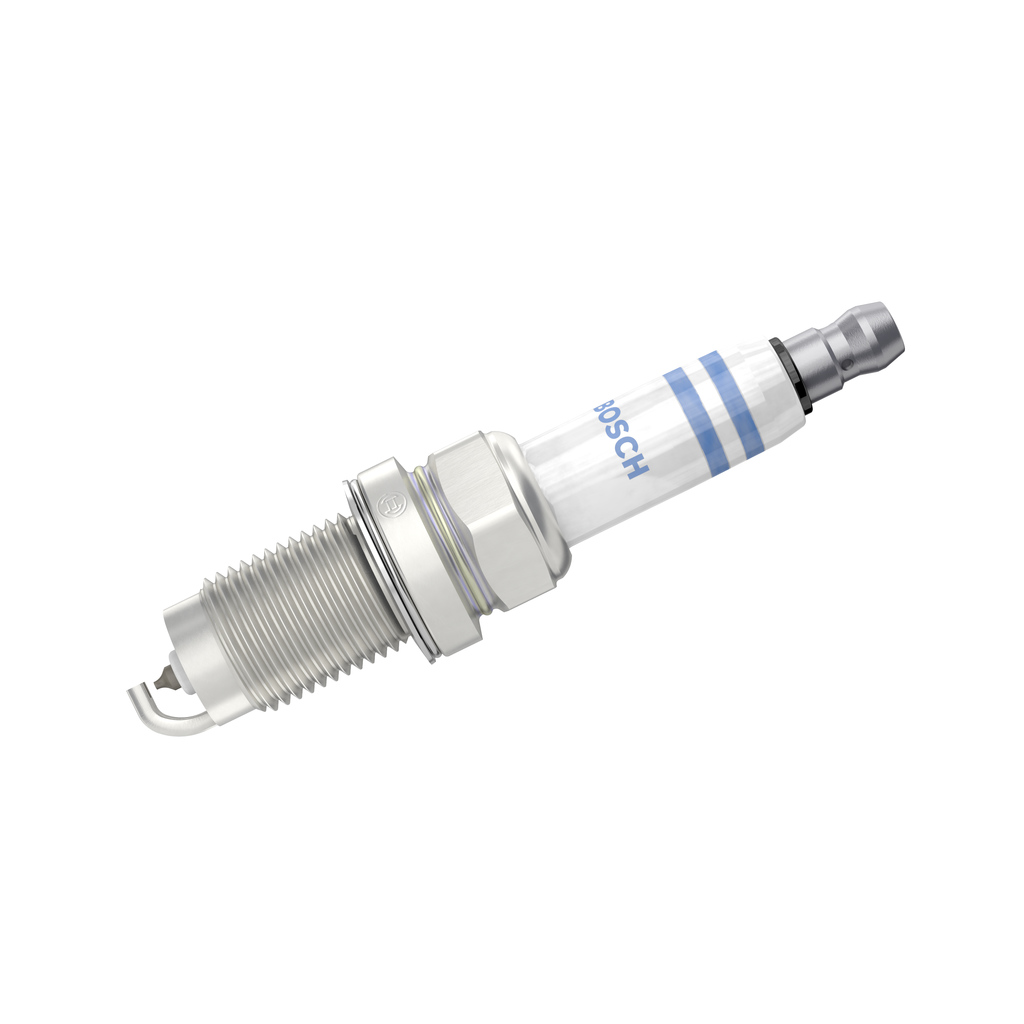


 BOSCH Spark plug
M 14 x 1,25, Spanner Size: 16 mm
BOSCH Spark plug
M 14 x 1,25, Spanner Size: 16 mm
- Defective ignition coils
Like the spark plugs, your car can’t produce power without them. They generate and convert the voltage required for the plugs to create a spark. They may fail due to electrical issues, damage or interference.
- A clogged air filter
The car air filter for the engine traps any foreign particles that may harm the unit, such as dirt and debris. Over time, it reaches its full capacity, preventing air from flowing through it efficiently. Without sufficient oxygen, the combustion process will be affected leading to a reduction in power.

- A camshaft position (CMP) sensor malfunction
The sensor’s readings are key for the ECU to calculate the exact timing of injection and ignition processes. If it goes bad, the engine power may be inconsistent, causing the car to stall, hesitate, or lurch forward under acceleration.
- A mass airflow (MAF) sensor malfunction
The MAF sensor, otherwise known as the car air flow meter, sends a signal to the ECU indicating how much air is required for acceleration. Based on this information, the unit makes the throttle open up or close to regulate the air flowing into the engine. If it malfunctions, the car may run too rich (too much fuel) or too lean (too much air) causing a reduction in power and fuel efficiency.
Top products related to this topic: